
Do Bed Bugs Only Target Legs? A question regarding the exclusive targeting of legs by bed bugs during their feeding behavior. These tiny, parasitic insects are known to feed on human blood, leaving behind itchy, red welts on exposed skin.
Understanding the biting patterns of bed bugs is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment of their infestations. Knowing where to expect the bites can help individuals take preventative measures, such as covering exposed areas while sleeping, and facilitate early detection, leading to prompt eradication efforts. Historically, the notion that bed bugs only bite legs has been a subject of debate, with recent research shedding light on their wider biting range.
This article delves into the complex feeding behavior of bed bugs, examining whether their bites are indeed limited to legs or if they target other body parts as well.
Would Bed Bugs Only Bite Legs?
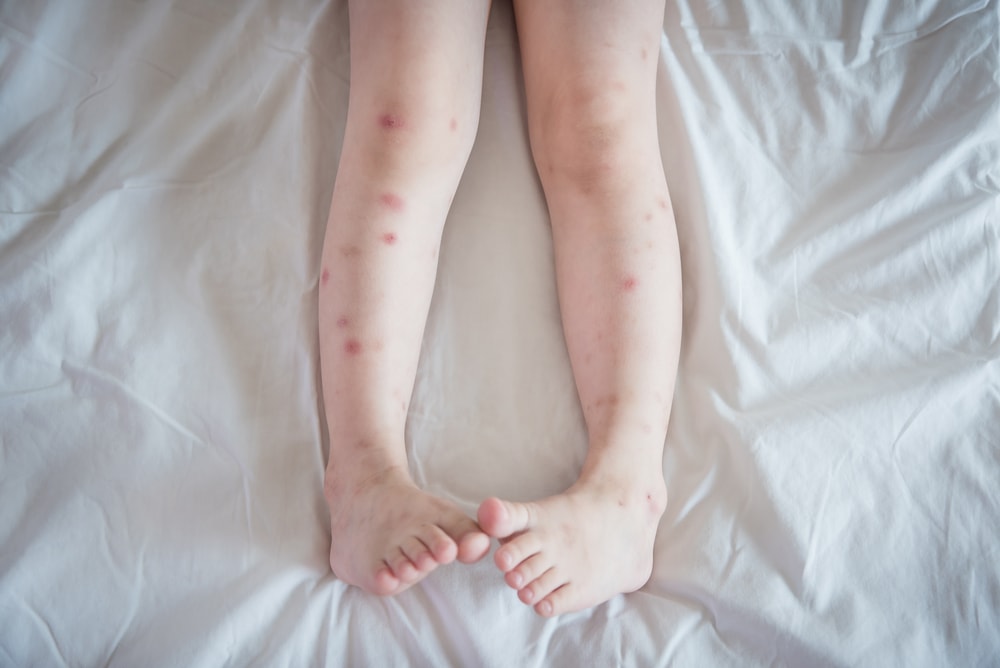
Understanding the feeding behavior of bed bugs is essential for effective prevention and treatment of their infestations. While it was traditionally believed that bed bugs only bite legs, recent research indicates a wider range of target areas. Here are ten key aspects to consider:
- Nocturnal feeding habits
- Attraction to exposed skin
- Preference for warm body parts
- Multiple bites in a localized area
- Itching and irritation at bite sites
- Potential for allergic reactions
- Transmission of diseases in rare cases
- Importance of early detection and treatment
- Challenges in eradication due to resistance
- Comprehensive pest management strategies
These aspects highlight the complex nature of bed bug infestations and the need for a multifaceted approach to their management. Understanding their feeding patterns, potential health risks, and effective control measures empowers individuals to protect themselves and their living spaces from these pests.
Nocturnal feeding habits
The nocturnal feeding habits of bed bugs significantly influence their target areas for biting. As these insects primarily feed at night, they seek out exposed skin that is easily accessible while their hosts are asleep and unaware. This behavior explains the common occurrence of bed bug bites on legs, as they are often left uncovered during sleep.
Furthermore, the warmth emitted by human legs makes them an attractive target for bed bugs. These pests are drawn to body heat, and the legs’ proximity to the body’s core temperature provides an ideal feeding environment. Additionally, the thinner skin on the legs may be more easily penetrated by bed bugs’ mouthparts, contributing to the higher incidence of bites in these areas.
Understanding the connection between nocturnal feeding habits and the targeting of legs by bed bugs is crucial for developing effective prevention and control strategies. By covering exposed skin while sleeping and implementing regular bed bug inspections, individuals can reduce their risk of being bitten and minimize the spread of these pests.
Read Also : Would Bed Bugs Only Bite Once? Unveiling the Mystery
Attraction to exposed skin
Bed bugs’ attraction to exposed skin plays a crucial role in determining their target areas for biting, including legs. These insects are primarily nocturnal feeders and rely on visual cues to locate their hosts. Exposed skin provides a clear signal to bed bugs, making it more likely for them to bite in these areas.
The warmth emitted by exposed skin further enhances its attractiveness to bed bugs. These pests are drawn to the warmth of human bodies, and exposed skin offers a direct path to access this heat source. Additionally, the thinner skin on the legs makes it easier for bed bugs to penetrate with their mouthparts, contributing to the higher incidence of bites in these areas.
Understanding the relationship between bed bugs’ attraction to exposed skin and their biting behavior has practical implications for prevention and control. By covering exposed skin while sleeping, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of being bitten. This is especially important for those who are particularly susceptible to bed bug bites or who have experienced infestations in the past.
In conclusion, bed bugs’ attraction to exposed skin is a critical component of their biting behavior, including their tendency to target legs. Understanding this connection can empower individuals to take effective preventative measures and minimize the impact of bed bug infestations.
Preference for warm body parts
Bed bugs exhibit a strong preference for warm body parts when selecting their target areas for biting, including legs. This behavior is primarily driven by their physiological need to regulate their body temperature. Bed bugs are ectothermic, meaning that they rely on external heat sources to maintain their optimal body temperature for activity and survival.
Human bodies emit heat, and certain areas of the body, such as the legs, neck, and face, tend to be warmer than others. Bed bugs are attracted to these warmer areas as they provide a stable and favorable environment for feeding. Additionally, the thinner skin in these areas makes it easier for bed bugs to penetrate with their mouthparts.
The preference for warm body parts is a critical component of bed bugs’ biting behavior. It influences their choice of target areas and contributes to the characteristic patterns of bites often observed on exposed skin. Understanding this preference is essential for developing effective prevention and control strategies.
In practice, this understanding can be applied in several ways. For instance, individuals can minimize their risk of being bitten by covering exposed skin while sleeping, especially in areas known to be attractive to bed bugs. Additionally, targeting warm body parts during bed bug inspections can increase the likelihood of detecting and eliminating these pests.
In summary, bed bugs’ preference for warm body parts plays a crucial role in their biting behavior, including their tendency to target legs. This understanding has significant implications for prevention and control efforts, empowering individuals to protect themselves and their living spaces from these pests.
Multiple bites in a localized area
Multiple bites in a localized area are a hallmark of bed bug infestations and play a significant role in understanding their biting behavior, including their tendency to target legs. This pattern of bites occurs due to bed bugs’ feeding habits and physiological needs.
When bed bugs feed, they typically insert their mouthparts into the skin and draw blood over several minutes. During this process, they may move slightly, resulting in multiple bites in close proximity. Additionally, bed bugs often target exposed areas of the body, such as the legs, which can lead to a concentration of bites in these areas.
Understanding the connection between multiple bites in a localized area and bed bug bites is crucial for several reasons. First, it helps distinguish bed bug bites from other insect bites or skin conditions. The presence of multiple bites in a localized area, particularly on exposed skin, is a strong indicator of a bed bug infestation.
Second, this understanding aids in the early detection of bed bug infestations. By inspecting for multiple bites in localized areas, especially on the legs, individuals can identify potential infestations early on and take prompt action to prevent their spread.
In summary, multiple bites in a localized area are an important component of understanding bed bug biting behavior, including their tendency to target legs. Recognizing this pattern can assist in the accurate diagnosis of bed bug infestations, facilitate early detection, and inform effective prevention and control strategies.
Itching and irritation at bite sites
Itching and irritation at bite sites are common reactions to bed bug bites, including those on the legs. These reactions can range from mild discomfort to severe inflammation, depending on individual sensitivity and the extent of the infestation.
- Skin irritation Bed bug bites inject an anticoagulant that prevents blood from clotting, leading to localized irritation and swelling. This can result in intense itching and discomfort, especially on sensitive areas like the legs.
- Allergic reactions Some individuals experience allergic reactions to bed bug bites, characterized by more severe swelling, redness, and itching. In rare cases, anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction, can occur.
- Secondary infections Constant scratching and irritation of bite sites can break the skin, creating an entry point for bacteria. This can lead to secondary infections, further complicating the healing process.
- Psychological impact The persistent itching and visible bite marks can cause psychological distress, affecting sleep quality, self-esteem, and overall well-being.
Itching and irritation at bite sites are significant aspects of bed bug infestations, impacting not only physical comfort but also mental and emotional health. Understanding these reactions and their potential consequences is essential for proper diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of bed bug-related issues.
Read Also: Would Bed Bugs Bite Only One Person? Bed Bug Behavior Explanation
Potential for allergic reactions
The potential for allergic reactions is an important aspect to consider when discussing whether bed bugs only bite legs. While not everyone who is bitten by a bed bug will develop an allergic reaction, it is a possibility that can have significant implications.
- Histamine release Bed bug bites inject a mild anesthetic and an anticoagulant into the skin. These substances can trigger the release of histamine, a chemical that causes blood vessels to dilate and become more permeable, leading to localized swelling and itching.
- Individual sensitivity The severity of an allergic reaction to bed bug bites can vary depending on the individual’s sensitivity to the insect’s saliva. Some people may experience only mild itching and swelling, while others may develop more severe reactions such as hives, blisters, or difficulty breathing.
- Multiple bites The number of bites can also influence the severity of an allergic reaction. A single bite may cause only minor irritation, but multiple bites can lead to a more pronounced reaction as more histamine is released into the skin.
- Anaphylaxis In rare cases, bed bug bites can trigger anaphylaxis, a severe and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction. Symptoms of anaphylaxis include difficulty breathing, swelling of the face and throat, and a rapid drop in blood pressure.
Understanding the potential for allergic reactions to bed bug bites is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Individuals who experience severe reactions should seek medical attention promptly. Additionally, preventive measures, such as using bed bug covers and regularly inspecting for signs of an infestation, can help reduce the risk of bites and subsequent allergic reactions.
Transmission of diseases in rare cases
While bed bugs primarily feed on blood, there is a rare possibility of disease transmission through their bites, even if they only bite legs. Understanding these potential risks is crucial for comprehensive prevention and treatment strategies.
- Trypanosoma cruzi This parasite, responsible for Chagas disease, can be transmitted through the feces of infected bed bugs. While rare, this condition can lead to heart and digestive issues.
- Hepatitis B Transmission of hepatitis B through bed bug bites is extremely uncommon. However, it highlights the potential for blood-borne pathogens to be transmitted in such scenarios.
- Bartonella quintana This bacteria, causing trench fever, can be transmitted via bed bug bites. Symptoms include fever, headaches, and muscle pain.
- Staphylococcal infections Bed bugs can carry and transmit staphylococcal bacteria, which can cause a range of skin and soft tissue infections.
The transmission of diseases through bed bug bites, though rare, emphasizes the importance of proper hygiene and prompt treatment of infestations. While the focus on leg bites is relevant, it is essential to remember that bed bugs can bite other exposed areas, increasing the potential for disease transmission. Effective pest control measures and seeking medical attention for any concerning symptoms are crucial for safeguarding health and well-being.
Importance of early detection and treatment
Early detection and treatment of bed bug infestations are crucial for several reasons, directly related to the question of whether bed bugs only bite legs. Firstly, early detection can prevent the spread of bed bugs to other areas of the home or to other people. If bed bugs are detected and treated early on, there is a lower risk of them becoming established in multiple rooms or infesting other people’s belongings.
Secondly, early treatment can help to reduce the severity of bed bug bites. Bed bug bites can cause itching, swelling, and irritation, and in some cases, they can lead to allergic reactions or secondary infections. Early treatment can help to minimize these symptoms and prevent them from becoming more severe.
Thirdly, early treatment can help to prevent the development of resistance to bed bug treatments. Bed bugs are becoming increasingly resistant to traditional pesticides, so it is important to treat infestations as early as possible to prevent the development of resistance. Early treatment can also help to reduce the overall cost of treatment, as it is less likely that multiple treatments will be necessary.
In conclusion, early detection and treatment of bed bug infestations are essential for preventing the spread of bed bugs, reducing the severity of bed bug bites, and preventing the development of resistance to bed bug treatments. If you suspect that you have a bed bug infestation, it is important to contact a pest control professional immediately.
Read Also: Should You Worry About Bed Bugs in the Bathroom?
Challenges in eradication due to resistance
The question of whether bed bugs only bite legs is closely related to the challenges in their eradication due to resistance. Bed bugs have developed resistance to traditional pesticides, making it more difficult to eliminate infestations. This resistance can lead to bed bugs becoming more persistent and widespread, increasing the likelihood of bites on various parts of the body, including the legs.
One of the reasons why bed bugs are becoming resistant to pesticides is their ability to adapt quickly to changes in their environment. Bed bugs can develop resistance to a pesticide after being exposed to it only a few times. This means that even if a pesticide is initially effective at killing bed bugs, it may become less effective over time as the bed bugs develop resistance.
The resistance of bed bugs to pesticides has led to the development of new and more effective treatments. However, these treatments can be more expensive and time-consuming than traditional pesticides. As a result, it is important to take steps to prevent bed bug infestations in the first place. These steps include:
- Inspecting used furniture and other items for bed bugs before bringing them into your home.
- Vacuuming and washing bedding and other fabrics regularly.
- Sealing up cracks and crevices where bed bugs can enter your home.
If you do find bed bugs in your home, it is important to contact a pest control professional immediately. They can help you to develop a treatment plan that is effective and safe for your family and pets.
By understanding the challenges of bed bug eradication due to resistance, you can take steps to prevent infestations and protect yourself from bites. This includes being aware of the potential for bed bugs to bite on various parts of the body, not just the legs, and taking appropriate precautions to minimize the risk of exposure.
Comprehensive pest management strategies
Comprehensive pest management (CPM) strategies play a critical role in addressing the question of “would bed bugs only bite legs.” CPM involves a holistic approach that encompasses a range of preventative and control measures to effectively manage pest populations, including bed bugs. By implementing these strategies, individuals can minimize the likelihood of bed bug infestations and reduce the risk of bites on various parts of the body, including the legs.
One of the key components of CPM is regular inspection and monitoring for signs of pest activity. This involves thoroughly checking areas where bed bugs are likely to hide, such as bed frames, mattresses, and. Early detection is crucial, as it allows for prompt intervention before an infestation becomes severe. By identifying and eliminating potential breeding grounds and harborage areas, CPM strategies can prevent the establishment of bed bug populations and reduce the risk of bites.
CPM also emphasizes the use of non-chemical methods to control bed bugs, such as vacuuming, steaming, and encasement. These methods are less likely to contribute to the development of resistance and can be effectively combined with targeted pesticide applications when necessary. By adopting an integrated approach, CPM strategies minimize the reliance on chemical treatments and reduce the overall risk of exposure to potentially harmful substances.
In practical terms, implementing CPM for bed bug management involves regular vacuuming of infested areas, using a steamer to kill bed bugs and their eggs, and encasing mattresses and box springs to prevent their spread. These measures, combined with proper sanitation and hygiene practices, can significantly reduce the population of bed bugs and minimize the likelihood of bites on the legs or other exposed areas of the body.
In summary, comprehensive pest management strategies are essential for addressing the question of “would bed bugs only bite legs.” By implementing CPM, individuals can effectively prevent or control bed bug infestations, reduce the risk of bites, and protect their health and well-being.
Read Also: Would Bed Bugs Bite Every Night?
FAQs on Bed Bug Bites
This FAQ section aims to address common questions and clarify aspects related to the topic of “Would Bed Bugs Only Bite Legs?” It provides concise answers to frequently encountered queries, offering valuable insights into bed bug behavior and bite patterns.
Do bed bugs exclusively bite legs?
Answer: While bed bugs often target exposed areas like legs, they can bite other body parts as well. Their feeding behavior is influenced by factors such as warmth, accessibility, and skin thickness.
Why are bed bug bites concentrated on legs?
Legs are typically exposed during sleep, making them easily accessible to bed bugs. Additionally, the thinner skin on the legs facilitates easier penetration by bed bugs’ mouthparts.
Can bed bug bites cause allergic reactions?
Yes, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to bed bug bites, ranging from mild itching to severe swelling and difficulty breathing. It is essential to seek medical attention if severe reactions occur.
How can I prevent bed bug bites on my legs?
To minimize the risk of bites on legs, wear protective clothing while sleeping, such as long pants and socks. Regularly inspect your bed and surrounding areas for signs of bed bugs, and implement effective pest control measures if necessary.
Are bed bug bites always visible?
Not necessarily. Bed bug bites can sometimes be subtle or go unnoticed, especially in individuals with less sensitive skin. It is important to be aware of other signs of an infestation, such as bloodstains on bedding or dark fecal spots.
Can bed bugs transmit diseases through their bites?
While rare, bed bugs have the potential to transmit certain diseases through their bites, including Chagas disease and Bartonella quintana infection. Maintaining good hygiene and promptly addressing infestations can help reduce the risk of disease transmission.
In summary, bed bugs do not exclusively bite legs, although they often target exposed areas. Understanding their bite patterns and implementing preventive measures can help minimize the risk of bites and potential health concerns. As we delve deeper into the topic, we will explore additional aspects of bed bug behavior, effective control strategies, and the importance of prompt treatment.
Transition to the next section: Bed bug infestations can be a challenging issue, but with proper knowledge and proactive measures, individuals can effectively protect themselves and their living spaces from these pests. The following section will delve into comprehensive strategies for preventing and controlling bed bug infestations.
Tips for Preventing and Controlling Bed Bug Bites
Implementing effective measures to prevent and control bed bug infestations is crucial for safeguarding your health and well-being. Here are a few practical tips to help you minimize the risk of bed bug bites and maintain a pest-free living environment:
Inspect regularly
Regularly check your bed, bedding, and surrounding areas for signs of bed bugs, such as blood stains, fecal spots, or shed skin.
Vacuum frequently
Vacuum your bed, floors, and upholstered furniture thoroughly to remove bed bugs, eggs, and shed skin. Dispose of the vacuum bag immediately after use.
Use bed bug covers
Encase your mattress and box spring in zippered, bed bug-proof covers to prevent infestations and trap existing bed bugs.
Wash bedding regularly
Wash your bedding, including sheets, pillowcases, and blankets, in hot water (at least 120F or 49C) and dry them on high heat to kill bed bugs and eggs.
Declutter and clean
Reduce hiding places for bed bugs by decluttering your home, removing clutter, and keeping areas clean and organized.
Seal entry points
Inspect your home for cracks and crevices where bed bugs may enter and seal them with caulk or expanding foam.
Avoid secondhand furniture
Exercise caution when acquiring used furniture, as it may harbor bed bugs. Thoroughly inspect any secondhand items before bringing them into your home.
Travel smart
When traveling, inspect your hotel room for signs of bed bugs before settling in. Keep your luggage off the floor and in a sealed plastic bag if possible.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of bed bug infestations and protect yourself from their bites. Early detection and prompt action are key to successful pest control. If you suspect a bed bug infestation, do not hesitate to contact a qualified pest control professional for assistance.
As we conclude this section on prevention and control, it is important to remember that managing bed bug infestations requires a comprehensive approach. In the next section, we will delve into the treatment options available for bed bug infestations, exploring various methods and their effectiveness.
Read Also: Would Bed Bugs Stay In One Room? A Comprehensive Guide!!!
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we have explored the question “Would bed bugs only bite legs?” and gained insights into the complex feeding behavior of these pests. While bed bugs often target exposed areas like legs, they can bite other body parts as well. Their bite patterns are influenced by factors such as warmth, accessibility, and skin thickness.
Two main points emerge from our discussion: First, understanding bed bug bite patterns is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. Early detection and prompt intervention can minimize the risk of bites and potential health concerns. Second, adopting comprehensive pest management strategies is essential for controlling bed bug infestations. By implementing preventive measures, such as regular inspections, vacuuming, and sealing entry points, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of infestations and protect their well-being.


